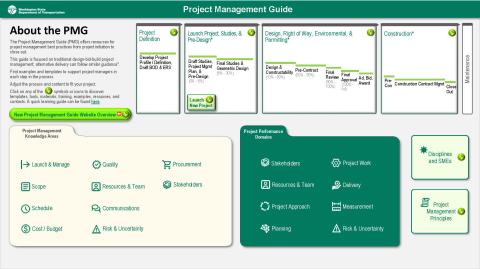
Project management guide
The Project Management Guide (PMG) offers resources for project management best practices from project initiation to close out.
This guide is focused on traditional design-bid-build project management; alternative delivery can follow similar guidance.
Find examples and templates to support project managers in each step in the process.
Adjust the process and content to fit your project, and always include all 10 project management knowledge areas.
Slow down on ice and snow.
It's easier to skid or lose control traveling at higher speeds. Give yourself more time to stop.
Carry chains, practice installing them.
Winter conditions could mean chains are required on your route. Practice putting them on your vehicle ahead of time.
Pack your winter car kit.
Carry extra supplies like warm clothing, ice scraper and brush, jumper cables and other emergency items.
